Overview

When standing, most people have a gap under the arch of their foot. Flat feet, or pes planus is the term used to describe collapsed arches, meaning that the entire sole of the foot rests partially or completely on the ground. A simple way to check to see if you have flat feet is to wet your feet and step onto a dry, flat surface. Step away from your footprint; if you see a complete footprint, you more than likely have flat feet. If you only see toes, the pads of your feet, and your heels, you probably do not have flat feet. People who have flat feet usually roll their feet over to the inner side when they walk. The feet may even appear to point outward because of this movement. In most cases, the condition cannot be prevented.
Causes
Fallen arches in adults are caused by several things. Below are some of the most common causes. Abnormalities present from birth. Torn or stretched tendons (resulting from foot injuries or foot strains). Inflammation or damage of the PTT (posterior tibial tendon). The PTT is responsible for connecting the middle of the arch to the ankle and lower leg. Dislocated or broken bones (also as a result of injury). Health problems like rheumatoid arthritis. Nerve problems. Other factors like diabetes, obesity, aging and pregnancy (these factors are known to increase the risk of fallen arches).
Symptoms
A significant number of people with fallen arches (flat feet) experience no pain and have no problems. Some, however, may experience pain in their feet, especially when the connecting ligaments and muscles are strained. The leg joints may also be affected, resulting in pain. If the ankles turn inwards because of flat feet the most likely affected areas will be the feet, ankles and knees. Some people have flat feet because of a developmental fault during childhood, while others may find that the problem develops as they age, or after a pregnancy. There are some simple devices which may prevent the complications of flat feet.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of flat feet or fallen arches can be made by your health practitioner and is based on the following. Clinical assessment involving visual gait assessment, as well as biomechanical assessment. A detailed family and medical history. A pain history assessment determining the location of painful symptoms. Physical palpation of the feet and painful areas. Imaging such as MRI or x-ray can be used by your practitioner to assist in the diagnosis.
Non Surgical Treatment
The treatment your podiatrist recommends will depend upon the trouble and pain you?re experiencing. Custom shoe inserts (orthotics) are most often recommended and are quite effective. Stretching exercises to loosen and strengthen the supporting tendons may also be recommended. Orthotic devices or bracing. To give your arch the support it needs, your foot and ankle surgeon may recommend an ankle brace or a custom orthotic device that fits into your shoe to support the arch. A short-leg cast or boot may be worn to immobilize the foot and allow the tendon to heal. Ultrasound therapy and stretching exercises may help rehabilitate the tendon and muscle following immobilization. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, help reduce the pain and inflammation. Your foot and ankle surgeon may recommend changes in your footwear.
Surgical Treatment

Procedures may include the following. Fusing foot or ankle bones together (arthrodesis). Removing bones or bony growths, also called spurs (excision). Cutting or changing the shape of the bone (osteotomy). Cleaning the tendons' protective coverings (synovectomy). Adding tendon from other parts of your body to tendons in your foot to help balance the "pull" of the tendons and form an arch (tendon transfer). Grafting bone to your foot to make the arch rise more naturally (lateral column lengthening).
When standing, most people have a gap under the arch of their foot. Flat feet, or pes planus is the term used to describe collapsed arches, meaning that the entire sole of the foot rests partially or completely on the ground. A simple way to check to see if you have flat feet is to wet your feet and step onto a dry, flat surface. Step away from your footprint; if you see a complete footprint, you more than likely have flat feet. If you only see toes, the pads of your feet, and your heels, you probably do not have flat feet. People who have flat feet usually roll their feet over to the inner side when they walk. The feet may even appear to point outward because of this movement. In most cases, the condition cannot be prevented.
Causes
Fallen arches in adults are caused by several things. Below are some of the most common causes. Abnormalities present from birth. Torn or stretched tendons (resulting from foot injuries or foot strains). Inflammation or damage of the PTT (posterior tibial tendon). The PTT is responsible for connecting the middle of the arch to the ankle and lower leg. Dislocated or broken bones (also as a result of injury). Health problems like rheumatoid arthritis. Nerve problems. Other factors like diabetes, obesity, aging and pregnancy (these factors are known to increase the risk of fallen arches).
Symptoms
A significant number of people with fallen arches (flat feet) experience no pain and have no problems. Some, however, may experience pain in their feet, especially when the connecting ligaments and muscles are strained. The leg joints may also be affected, resulting in pain. If the ankles turn inwards because of flat feet the most likely affected areas will be the feet, ankles and knees. Some people have flat feet because of a developmental fault during childhood, while others may find that the problem develops as they age, or after a pregnancy. There are some simple devices which may prevent the complications of flat feet.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of flat feet or fallen arches can be made by your health practitioner and is based on the following. Clinical assessment involving visual gait assessment, as well as biomechanical assessment. A detailed family and medical history. A pain history assessment determining the location of painful symptoms. Physical palpation of the feet and painful areas. Imaging such as MRI or x-ray can be used by your practitioner to assist in the diagnosis.
Non Surgical Treatment
The treatment your podiatrist recommends will depend upon the trouble and pain you?re experiencing. Custom shoe inserts (orthotics) are most often recommended and are quite effective. Stretching exercises to loosen and strengthen the supporting tendons may also be recommended. Orthotic devices or bracing. To give your arch the support it needs, your foot and ankle surgeon may recommend an ankle brace or a custom orthotic device that fits into your shoe to support the arch. A short-leg cast or boot may be worn to immobilize the foot and allow the tendon to heal. Ultrasound therapy and stretching exercises may help rehabilitate the tendon and muscle following immobilization. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, help reduce the pain and inflammation. Your foot and ankle surgeon may recommend changes in your footwear.
Surgical Treatment

Procedures may include the following. Fusing foot or ankle bones together (arthrodesis). Removing bones or bony growths, also called spurs (excision). Cutting or changing the shape of the bone (osteotomy). Cleaning the tendons' protective coverings (synovectomy). Adding tendon from other parts of your body to tendons in your foot to help balance the "pull" of the tendons and form an arch (tendon transfer). Grafting bone to your foot to make the arch rise more naturally (lateral column lengthening).








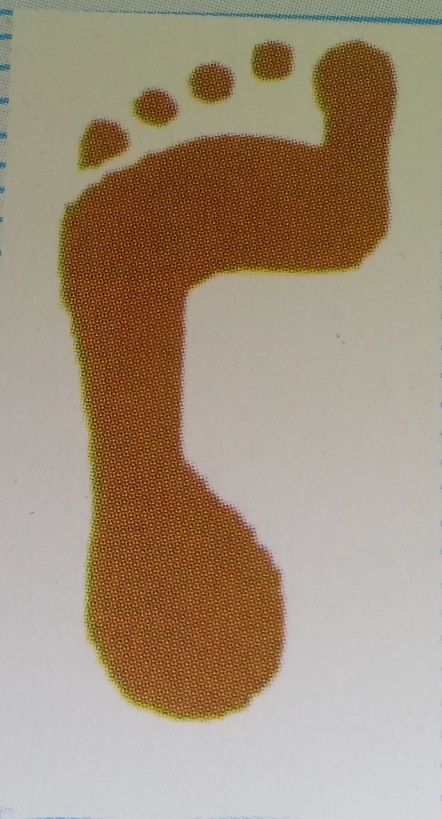

 The Achilles tendon is the largest and most vulnerable tendon in the body. It joins the gastrocnemius (calf) and the soleus muscles of the lower leg to heel of the foot. The gastrocnemius muscle crosses the knee, the ankle, and the subtalar joints and can create stress and tension in the Achilles tendon . Tendons are strong, but not very flexible so they can only so far before they get inflammed and tear or rupture.
The Achilles tendon is the largest and most vulnerable tendon in the body. It joins the gastrocnemius (calf) and the soleus muscles of the lower leg to heel of the foot. The gastrocnemius muscle crosses the knee, the ankle, and the subtalar joints and can create stress and tension in the Achilles tendon . Tendons are strong, but not very flexible so they can only so far before they get inflammed and tear or rupture.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
